Given an m x n board of characters and a list of strings words, return all words on the board.
Each word must be constructed from letters of sequentially adjacent cells, where adjacent cells are horizontally or vertically neighboring. The same letter cell may not be used more than once in a word.
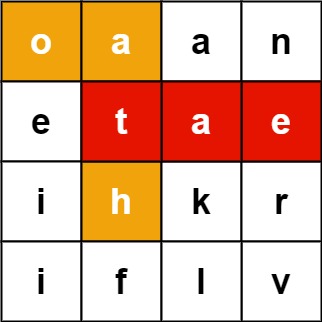
Input: board = [["o","a","a","n"],["e","t","a","e"],["i","h","k","r"],["i","f","l","v"]], words = ["oath","pea","eat","rain"]
Output: ["eat","oath"]
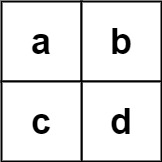
Input: board = [["a","b"],["c","d"]], words = ["abcb"]
Output: []
m == board.length
n == board[i].length
1 <= m, n <= 12
board[i][j] is a lowercase English letter.
1 <= words.length <= 3 * 104
1 <= words[i].length <= 10
words[i] consists of lowercase English letters.
All the strings of words are unique.
from typing import List
class Solution:
def dfs(self, board: List[List[str]], word: str, wordid: int, x:int, y:int ):
if x < 0 or y < 0 or x >= len(board) or y >= len(board[0]):
return False
if not board[x][y]:
return False
if wordid >= len(word):
return False
if board[x][y] != word[wordid]:
return False
if wordid == len(word) -1:
return True
temp = str(board[x][y])
board[x][y] = " "
if self.dfs(board, word, wordid+1, x+1, y) or self.dfs(board, word, wordid+1, x-1, y):
board[x][y] = temp
return True
if self.dfs(board, word, wordid+1, x, y+1) or self.dfs(board, word, wordid+1, x, y-1):
board[x][y] = temp
return True
board[x][y] = temp
return False
def checkin(self, board, word: str):
myset = set()
wset = set()
for a in board:
myset.update(a)
wset.update([i for i in word])
return len(myset & wset) == len(wset)
def findWord(self, board: List[List[str]], word: str) -> List[str]:
for x in range(len(board)):
for y in range(len(board[0])):
if self.dfs(board, word, 0, x, y):
return True
return False
def findWords(self, board: List[List[str]], words: List[str]) -> List[str]:
result = []
for word in words:
if not self.checkin(board, word):
continue
if self.findWord(board,word):
result.append(word)
return result
pass
board = [["o","a","a","n"],["e","t","a","e"],["i","h","k","r"],["i","f","l","v"]]
words = ["oath","pea","eat","rain"]
print(Solution().findWords(board, words))
board = [["a","b"],["c","d"]]
words = ["abcb"]
print(Solution().findWords(board, words))
如果只是 DFS 肯定會超時,所以提前檢查 board 裡有沒有 word 要的字,沒的話就跳過這個案例。
這方法其實有點取巧...測資如果刁鑽一點也不能過。

johnting 像是什麼刁鑽的測資?
剛剛好符合 包含這個字,但是長度上會超時的測資
可以丟到 LeetCode 上的Test Case測測看
DFS+IF先判斷 不是就是Backtracking嗎???不會取巧啊
我是先判斷這段測資可不可用,之後才使用 DFS 的。
原因在於我觀察到一段超時的測資,board 只有 [a, b],而 word 是ababababab 加上一個其他英文。
也因此我可以事先判斷 board 內有沒有 word 的單字,來避過整段測資。但要是出題者在 board 中放入那些英文單子,那麼這篩選就沒有意義。